Create A PostgreSQL Database
After initializing the environment and deploying the root application, in the Argo-CD web UI (see how to access the web UI in the previous section), you should see the root-app, postgresql, ext-postgres-operator, and sample-pg-app:
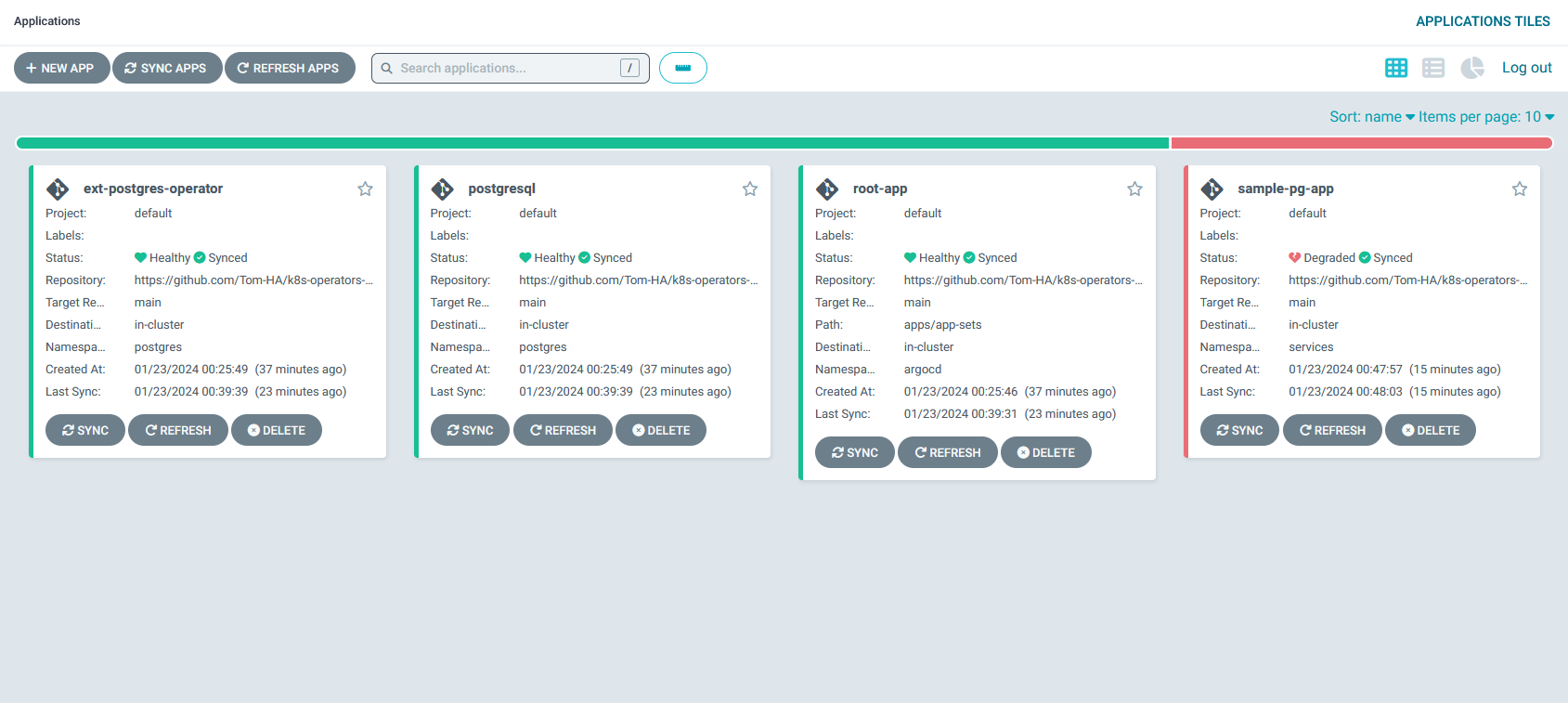
Oh no, the sample-pg-app is not healthy…
Let’s click on the sample-pg and investigate the failing pod:
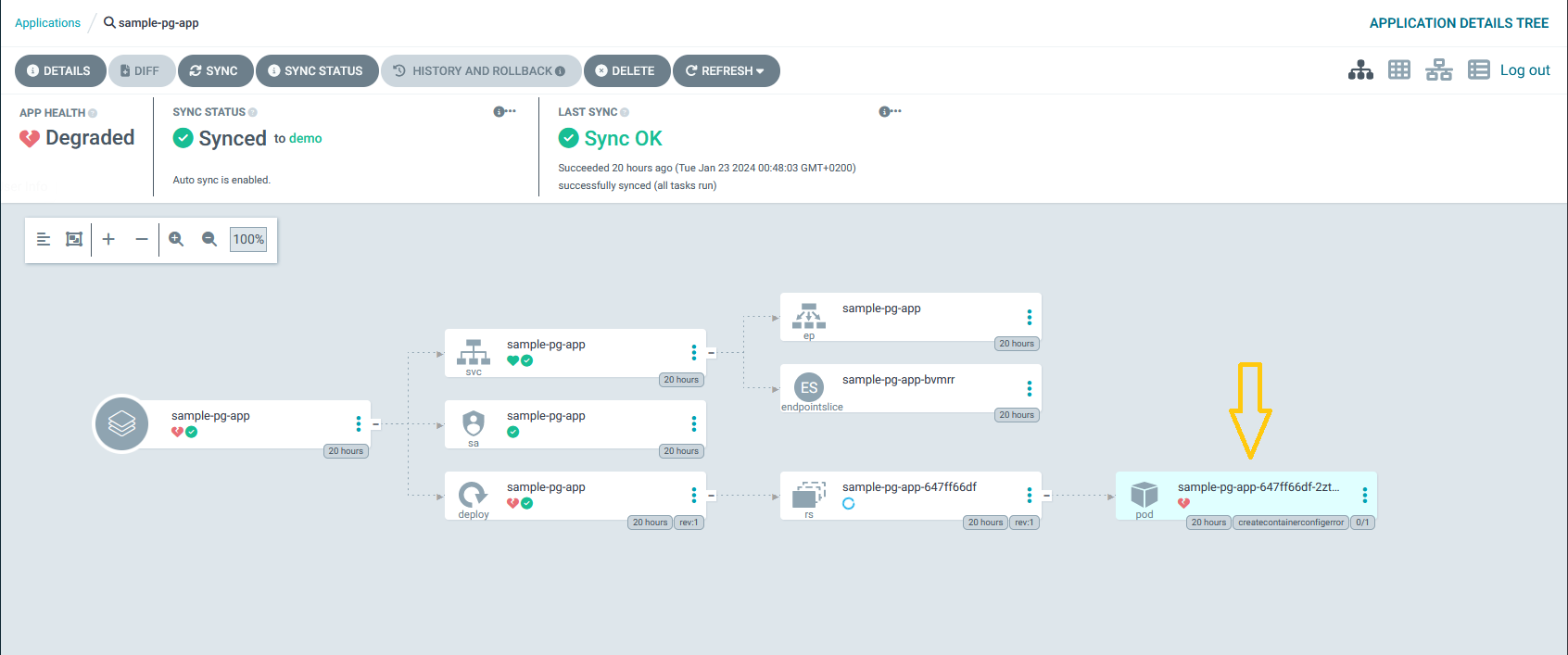
As you can see, the Pod is missing a Kubernetes Secret:
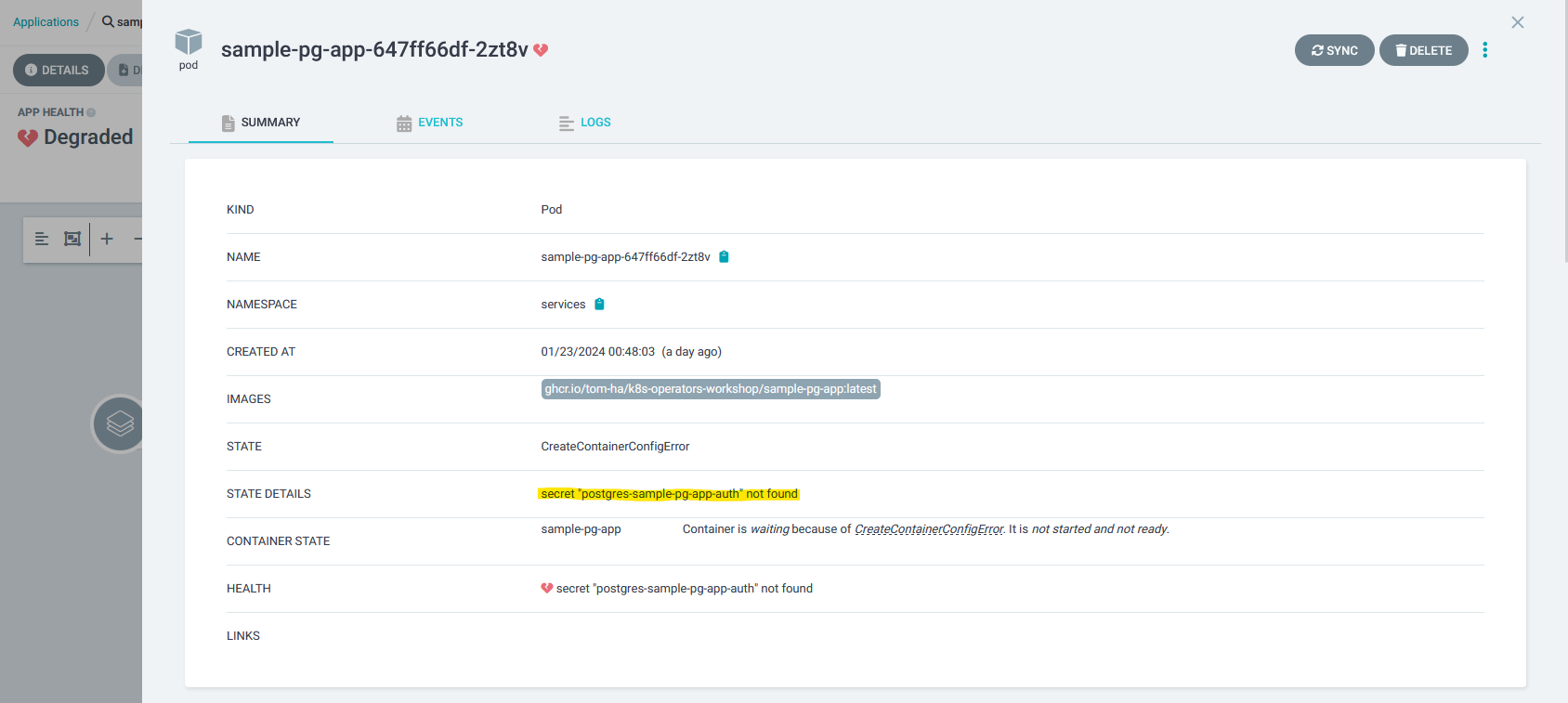
Our sample-pg-app is expecting a Kubernetes secret with authentication details to the PostgreSQL database
You can check the code and the chart under the sample-pg-app folder.
To fix it, we are going to implement a Postgres CR which will instruct the ext-postgres-operator to provision a new database.
Add the following .yaml to apps/services/sample-pg-app/hooks, then commit and push your changes.
Make sure the file name you choose ends with .yaml, for example, database.yaml.
apiVersion: db.movetokube.com/v1alpha1
kind: Postgres
metadata:
name: sample-pg-app-db
namespace: services
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PreSync # Executes prior to the sync operation.
spec:
database: sample-pg-app-db # Name of database created in PostgreSQL
dropOnDelete: false # Set to true if you want the operator to drop the database and role when this CR is deleted (optional)After you pushed your changes, in the web UI, go back to the sample-pg-app page, you should see a new postgres resource!
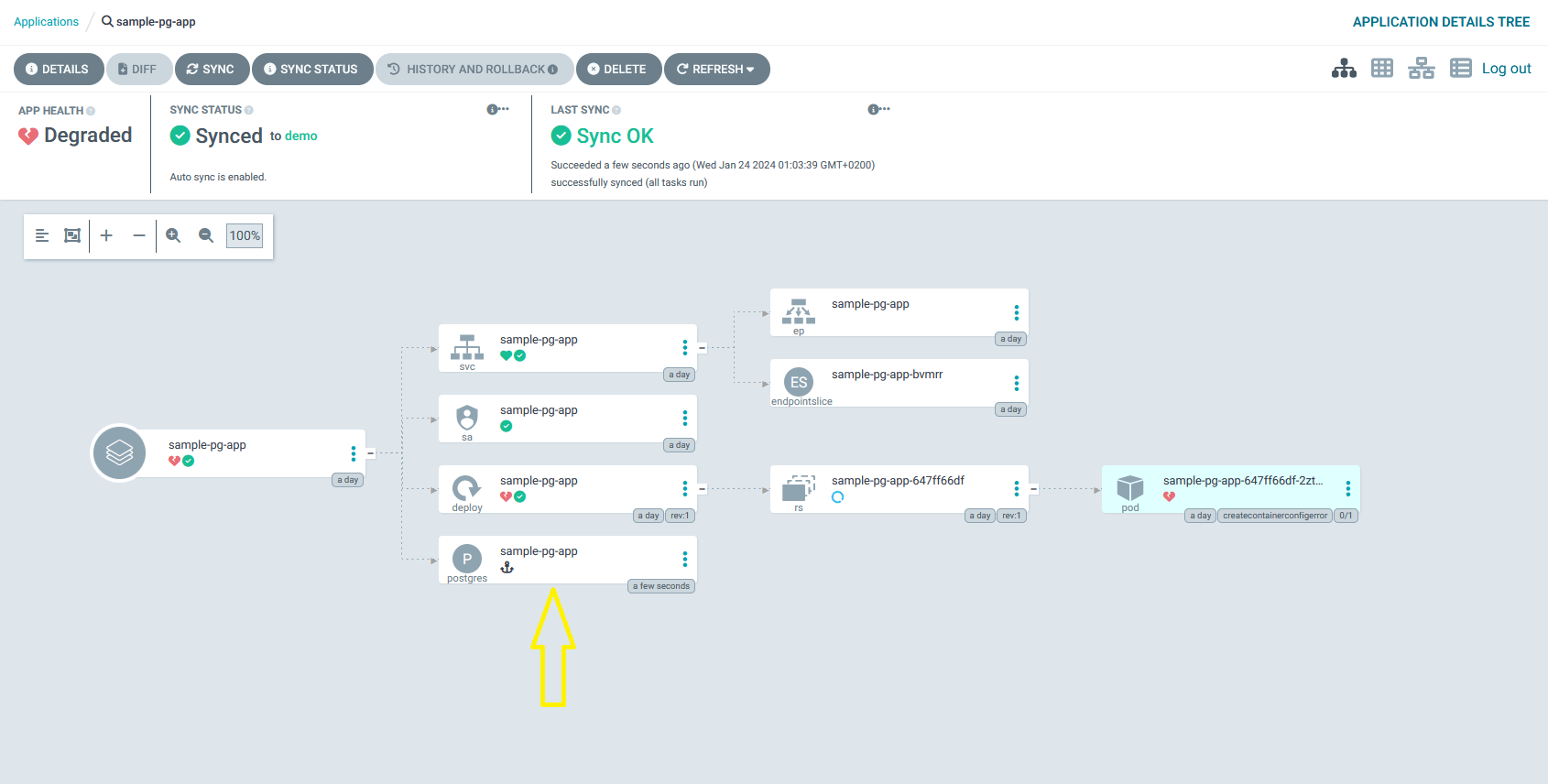
If you don’t see the postgres resource, you might need to wait for Argo-CD to sync the changes from your repository, alternatively, you can trigger a sync manually by clicking on the sync button and then synchronize.
🎉 Congratulations! You’ve just provisioned a database declaratively with GitOps and a Kubernetes operator!
But wait, the sample-pg-app still needs a Kubernetes secret with credentials to connect to the database.
That, will be covered in the next slide.
Last updated 26 Feb 2024, 22:53 +0200 .